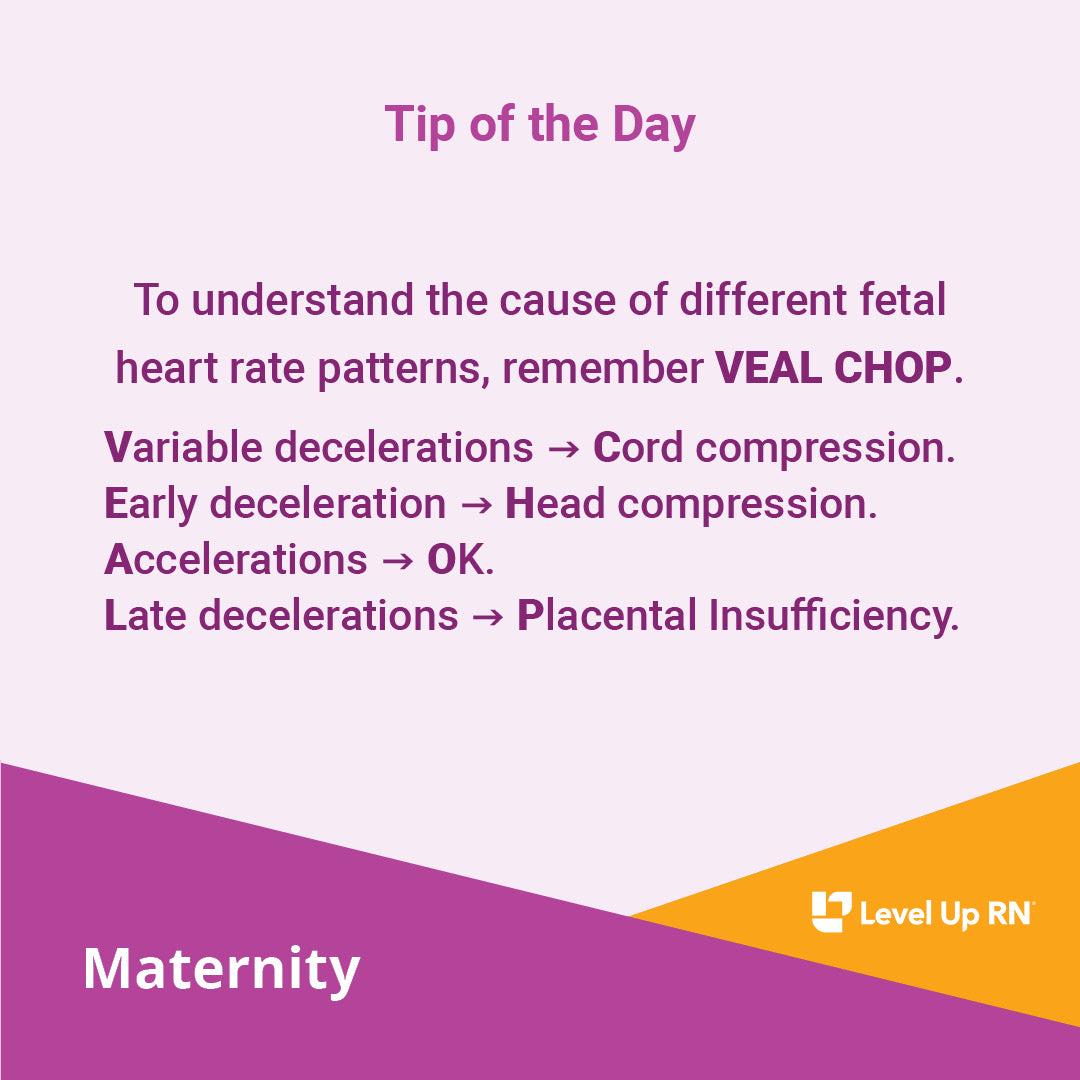
To understand the cause of different fetal heart rate patterns, remember VEAL CHOP.
Variable decelerations -> Cord compression.
Early deceleration -> Head compression.
Accelerations -> OK.
Late decelerations -> Placental Insufficiency.
What is the VEAL Chop Method for Nursing?
The VEAL chop method for nursing stands for variable deceleration, early deceleration, accelerations, and late decelerations. And the chop stands for cord compression, head compression, oxygenated or OK, and placental insufficiency. It is a mnemonic that helps nurses determine the cause of fetal heart change during labor.
What Does the VEAL CHOP Method Stand For?
V: Variable decelerations: stand for abrupt, visually apparent decreases in the fetal heart rate
E: Early deceleration: often refer to symmetrical decreases and return of fetal heart rate (FHR) that is typically associated with a uterine contraction.
A: Accelerations: signifies an abrupt increase in fetal heart rate above the established baseline.
L: Late decelerations: are the visually apparent, gradual decrease in the fetal heart rate typically following the uterine contraction.
C: Cord compression: can cause for variable decelerations in a heartbeat.
H: Head compression: could cause fetal heart rate decelerations during labor.
O: Oxygenated/OK: Fetal heart rate acceleration is a good indicator that there is no hypoxemia in the fetus
P: Placental insufficiency: indicated by late decelerations and a gradual decrease in heart rate lasting 30 seconds or more following a uterine contraction.